Recent Searches
Popular Attractions
Sydney
Melbourne
Gold Coast
Phillip Island
Brisbane
Featured Events in Tokyo in May 2025 (July Updated)
Are you interested in Tropical Palm Tree Paint Night?
245 people have participated in this
poll
Yes
No




50%



50%
Type
Location
Event Status
Popularity
Start Time

Ghibli 3D sculpture exhibition | Warehouse TERRADA B&C HALL
The Ghibli 3D Modeling Exhibition, which explores the appeal of Studio Ghibli works, will be held at Warehouse Terada B&C HALL/E HALL in Tennoz, Tokyo from Tuesday, May 27th.
Studio Ghibli works, including the movie "How Do You Live?", which has been released in over 80 countries and regions, are now being watched all over the world. Behind the scenes, there were people in each country and region who loved the works and tried to spread them over a long period of time. This exhibition will introduce famous scenes from the movies through 3D models, tracing how overseas partners distributed the works. The 3D Modeling Exhibition is the origin of the full-scale Studio Ghibli exhibition that began in 2003, and will return to Tokyo after 22 years of evolution.
Of particular interest is the Savoia S-21 flying boat that appears in the movie "Porco Rosso". The impressive flying boat, created based on the assumption that it "really existed," will look like it is about to take off from Warehouse Terada at any moment.
The event will run from May 27th (Tuesday) to September 23rd (Tuesday, national holiday). The "Ham Ramen" that was on sale at the "Friday Road Show and Ghibli Exhibition" two years ago and became a hot topic will be back at the water facility "T-LOTUS M" next to the venue. In addition, tickets will be sold in combination with the Ghibli Museum in Mitaka and tickets linked to hotel accommodation plans.

ACN Ramses the Great and the Gold of the Pharaohs | Tokyo
Ramses The Great and the Gold of the Pharaohs will feature 183 pieces of rare artefacts from ancient Egypt that focus on the almighty pharaoh, Ramses The Great and it will be the largest collection of artefacts on Ramses II to ever leave Egypt. This spectacular exhibition will also boast the FIRST ever virtual walkthrough of Ramses II’s famous temples as well as a full-length documentary ever produced on Ramses II’s tomb.

Immersive Theater on Neo-Japonism: From Ancient Art to Anime | Tokyo National Museum
For millions of years, unique aesthetics have been born on the islands of Japan and have been passed down from generation to generation.
From Jomon earthenware, Haniwa, Erika, armor, and ukiyo-e, to the popular anime that has taken the world by storm, this is an immersive theater that combines NHK's high-definition video technology with “New Wafuism”.
The New Wafuism Theater is an immersive theater that incorporates NHK's high-definition video technology.
In the theater, you will be able to experience Japanese culture through a time-traveling journey with national treasures and important cultural properties of the Tokyo National Museum.
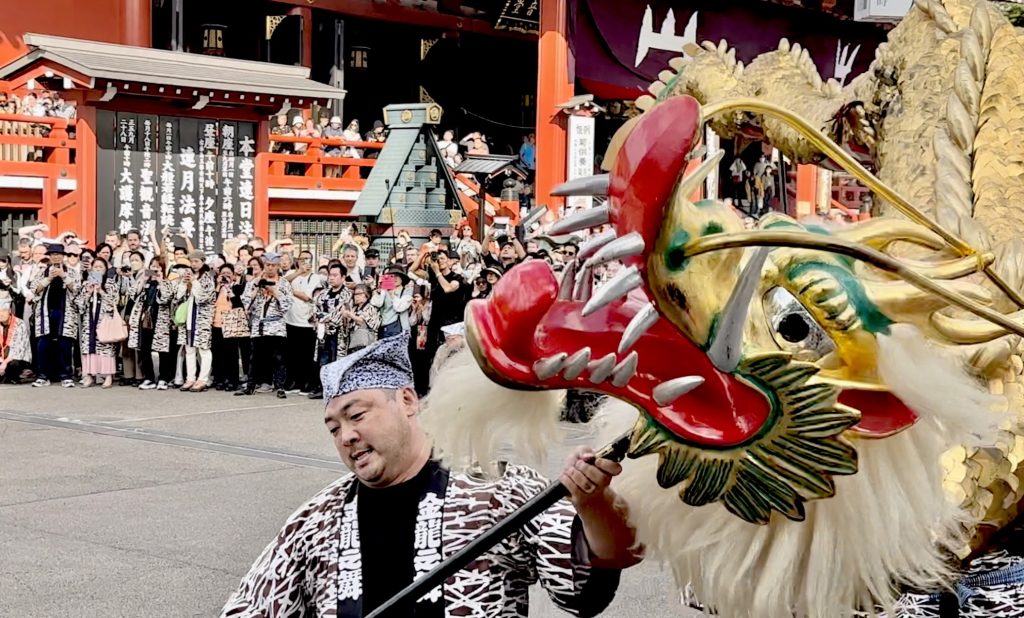

Asakusa Temple Golden Dragon Dance Festival | Tokyo
The official name of Sensoji Temple comes from the Golden Dragon Mountain, and it is called "Golden Dragon Mountain Sensoji Temple", and the name "Golden Dragon Dance" comes from the name of this mountain. "Golden Dragon Dance" is a dance that started in 1958 to commemorate the reconstruction of the main hall of Sensoji Temple, Kannon Hall. This dance is based on the story of Guanyin Bodhisattva enshrined in Sensoji Temple. According to legend, she appeared as a golden dragon that descended from the sky, and overnight she created a thousand pine trees that symbolize a good harvest.
The 18-meter-long, 88-kilogram shining golden dragon dances gorgeously to the music of the celebration, and this scene is absolutely impressive.

Satellites: Nicolas Winding Refn and Hideo Kojima | Tokyo
Japanese game auteur Hideo Kojima, the mind behind Death Stranding and the Metal Gear series, has revolutionised interactive storytelling with his cinematic sensibility. Danish director Nicolas Winding Refn, celebrated for Drive and Only God Forgives, is known for his stylised, meditative explorations of violence and human nature. Bound by mutual respect and a fascination with the convergence of their mediums, the two artists share a decade-long friendship that has sparked artistic collaborations across film and video games. The two visionary creators now reunite in Tokyo for an ambitious installation. From April 18 to August 25, Prada Aoyama hosts ‘Satellites: Nicolas Winding Refn with Hideo Kojima’, an exhibition that invites visitors into a retro-futuristic space where Refn and Kojima appear across six exposed television screens together shaped like a spaceship, engaging in dialogue on identity, death and creativity.The journey continues in an adjacent dressing room filled with cassette tapes, interweaving AI-translated soundbites and film soundtracks, allowing guests to craft their own narrative from fragments of conversation. Blurring the lines between analogue and digital, film and games, ‘Satellites’ explores human connection in an age of technological fusion.

Design Neo | Tokyo
"Design Ah! Neo" is an exhibition that expands the concept of the program "Design Ah! Neo" currently airing on NHK Educational TV into an experiential space. It has been held as a "Design Ah! Exhibition" at 21_21 DESIGN SIGHT in 2013, and at six museums across the country, including the Miraikan, the National Museum of Emerging Science and Innovation, and the Toyama Prefectural Museum of Art from 2018 to 2021. The third "Design Ah! Neo" exhibition will exhibit new works with new themes, while retaining the concept of encouraging children to enjoy various thoughts and discoveries about design.
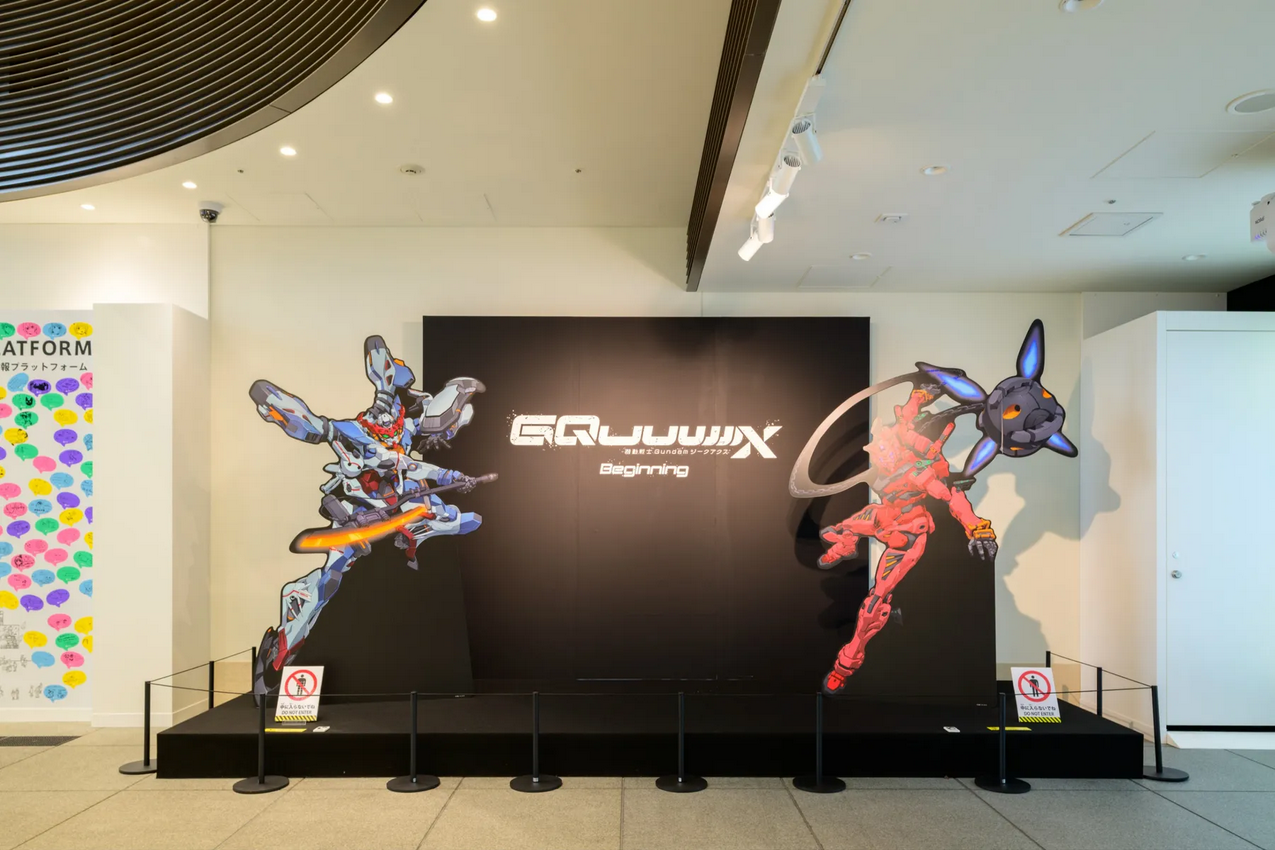

"Mobile Suit Gundam GQuuuuuuX -Beginning-" Special Exhibition | Tokyo
A special exhibition of the latest Gundam series, which is also a hot topic for its TV broadcast!
Anime Tokyo Station, an exhibition center for anime that utilizes Japanese anime content with a strong fan base around the world, is holding a special exhibition of the theatrical advance version of "Mobile Suit Gundam GQuuuuuX (Gi-Q Axe) -Beginning-".
This work is the latest Gundam series work directed by Kazuya Tsurumaki, which attracted a lot of attention as it was the first collaboration between Studio Khara, the creator of the "Evangelion" series, and Sunrise, the creator of the Gundam series. The theatrical advance version, which was screened ahead of the TV series broadcast, with some episodes reconstructed, was very popular and continues to attract attention even after the anime began broadcasting in April this year.
The special exhibition will feature scene cuts from the theatrical advance version of "Mobile Suit Gundam GQuuuuuX -Beginning-", which was screened ahead of the TV series broadcast, looking back on famous scenes from the work. Other attractions include standees of characters and mobile suits, including the main character Amaterasu Yuzuriha (Machu), a photo spot that recreates scenes from the series, and valuable production materials such as scripts. There is also a corner where you can take AR photos with motifs of characters.

"Pac-Man" TOKYO Night & Light | TMG Building Citizens' Plaza
Tokyo Metropolitan Government has created a new tourist resource for nighttime viewing by using the exterior wall of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Building No. 1 as a screen to express a variety of art with light and sound, and to perform projection mapping all year round in order to activate and revitalize nighttime tourism.
This time, as the 45th anniversary is approaching next year, the Tokyo Metropolitan Government will begin showing works using the world-famous "Pac-Man".
The game board appears on the outer wall of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Building, and Pac-Man, who is making a futuristic scene, eats up everything vividly. The music of the game of Pac-Man, which has a futuristic feel, and the music of the highly friendly soundtrack maker Mr. Haraguchi Sasuke have produced. Please enjoy the collaborative work of Pac-Man and Tokyo that can only be seen in the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Building.

| Tokyo
Are you ready for a great party?
Join Kuromi, My Melody and Hapidanbui for an exciting exhibition!
Dive into interactive displays, dance to hit music, and enjoy hands-on fun.

School Life of the Peanuts Gang | Snoopy Museum Tokyo
When Charlie Brown and his sister Sally get on the school bus with their friends and head off to school, various events await them. They meet unique friends and teachers. Classes are conducted day by day, and sometimes there are tense presentations, and as a reward, there are dance events. When they get home, they do their homework, and during summer vacation, they meet new people at summer camp. The school life of the Peanuts gang is a familiar, bittersweet experience. Enjoy school life with the Peanuts gang through about 45 carefully selected comics.
Reverberation from the Universe | Yayoi Kusama Museum
From a young age, Kusama has suffered from visual and auditory hallucinations. Her mental health condition has had a tremendous impact on the artist’s creative activities. In the 1950s, driven by her own obsessions, Kusama created an enormous number of drawings, resulting in an opportunity to make her breakthrough as an artist. After relocating to the United States in 1957, the artist began to create a series of works that could be described as ritual of “self-obliteration,” where all existence is engulfed in infinitely repetitive patterns such as polka dots and nets while the self is immersed into a boundless world. These works express a desire for salvation from psychological disorders and simultaneously reflect her intention to liberate society from absurd oppression through happenings and other forms of expression.

Renoir / Cézanne – Pioneers of Modernity | Mitsubishi Ichigokan Museum
This is a touring, international exhibition designed and organised by
the Musée de l'Orangerie in Paris, France, focusing together, for the
first time, on two Impressionist/Post-Impressionist painters, Renoir and
Cézanne.Featuring masterpieces like Renoir’s “Two Young Girls at the
Piano” and Cézanne’s “Portrait of the Artist’s Son”, the exhibition
explores the origins of modern art through approximately fifty works,
including portraits, still lifes, and landscapes by these two great
masters, as well as pieces by Picasso, who was influenced by
them.Realised through cooperation between the Musée de l'Orangerie and
the Musée d'Orsay, the exhibition travels the world, showing in Milan,
then Martigny (Switzerland) and Hong Kong, before appearing at
Mitsubishi Ichigokan Museum, Tokyo, the only Japanese venue for the
show.We hope that audiences will delight in the connections between
Renoir and Cézanne, and in the extraordinary artistic expression of
these two great masters who produced such unconstrained and diverse work
on the eve of the birth of modern art.

Miffy's 70th Anniversary Exhibition | Tokyo
Miffy, born in 1955 by Dutch picture book author and graphic designer Dick Bruna, will celebrate its 70th anniversary in 2025. To commemorate this, we will hold the "Miffy 70th Anniversary Exhibition" with the theme "More, More, Miffy".
This exhibition will display the original drawings and sketches of all 32 picture books in the Miffy series, including the original drawings of "Miffy Stays Over" (1988) and "Miffy's Favorite Grandma" (1996), which will be the first time they visit Japan. In addition, early paintings, paperback bindings, and poster designs will also be on display. More than 200 works and materials will explore the charms of Miffy and Bruna. This exhibition will introduce the charm of Miffy from every angle, including her heartwarming story, adorable characters, rhythmic words, graphical colors, lines and composition, allowing you to love Miffy more deeply, more enjoyably and even more.
![G-DRAGON 2025 WORLD TOUR [Übermensch] IN JAPAN | Tokyo Dome](https://ak-d.tripcdn.com/images/0104l12000junwvs25667.jpg)
G-DRAGON 2025 WORLD TOUR [Übermensch] IN JAPAN | Tokyo Dome
AnyPASS TicketExchangeNote
G-DRAGON, a megastar with world-class iconic influence, has officially announced the detailed information of the highly anticipated "G-DRAGON 2025 WORLD TOUR [Übermensch]". This world tour, jointly presented by Galaxy Corporation and AEG presents, will bring a thrilling experience to fans around the globe.
The tour kicks off with two shows at the Goyang Stadium in South Korea, and tickets for both of these performances have already been sold out. Through this tour, G-DRAGON will showcase his unparalleled artistry and groundbreaking performances to audiences worldwide.
After a seven-year hiatus from his solo activities, he made a memorable comeback in 2024 with the release of the single "POWER". The song quickly climbed to the top of the charts and received widespread acclaim. Riding on this momentum, G-DRAGON released his much-anticipated third studio album, "Übermensch", on February 25th. This album, which features tracks like "TOO BAD" and "DRAMA", has received overwhelming praise from both fans and critics.
"Übermensch" ushers in a bold new chapter in G-DRAGON's career, solidifying his reputation as an artist who is constantly evolving and pioneering new artistic frontiers.

Shaun the Sheep Exhibition with Wallace and Gromit | Tokyo
Miniature photographer and mimicry artist Tatsuya Tanaka
"Shaun the Sheep Exhibition with Wallace and Gromit" will be held at the Tokyo Anime Center.
This year marks the 30th anniversary of the birth of the British clay animation "Shaun the Sheep." To commemorate this, "Shaun the Sheep Exhibition with Wallace and Gromit" will be held at the Tokyo Anime Center in Shibuya, Tokyo.
In the movie "Wallace and Gromit: A Close Shave," Wallace's loyal dog Gromit finds a sheep that wanders into the kitchen and eats everything. Thirty years later, this skinny, hungry sheep is still loved as a "fluffy superstar" in 170 countries around the world.
Thirty years have passed since Wallace gave him the name "Shaun." Why does this silent character continue to attract fans around the world? And what is the enduring appeal of the "Wallace and Gromit" series that started it all? This exhibition will take you behind the scenes of this masterpiece from the British company Aardman Animations through approximately 260 pieces of concept art and dioramas actually used in filming, as well as a special exhibition that will be shown for the first time in the world. Many original goods will also be on sale only at the venue, so please wait for further details.
There will also be rare exhibits from the "Shaun the Sheep" and "Wallace and Gromit" series that will be shown in Japan for the first time. From "Shaun the Sheep," there will also be a world premiere of a set that recreates a scene from the main story of the latest TV series 7, which is scheduled to be released this year. From the "Wallace & Gromit" series, Japanese fans will be shown for the first time exhibits that appeared in memorable scenes from "Wallace & Gromit: A Hard Day's Blow," the latest work from Aardman Animations that won the 78th BAFTA Award for Best Animated Film.
And from "Wallace & Gromit: A Close Shave," Shaun's screen debut, which is celebrating its 30th anniversary since its release and has ties to both the "Shaun the Sheep" and "Wallace & Gromit" series, precious exhibits used in the filming of the film will be introduced. In addition, following on from the previous "Shaun the Sheep Exhibition," there will be a special exhibition of collaborative works with miniature photographer and mimesis artist Tatsuya Tanaka. Why not take this opportunity to visit?

Joan Miró Exhibition | Tokyo Metropolitan Art Museum
Joan Miró (1893-1983) is one of the most important Spanish artists of the 20th century, as famous as Picasso and Dali. His creations experienced changes from Fauvism, Realism to Surrealism, and finally established his own unique style. His paintings are famous for their strong colors, imagination and poetry. This exhibition will present the artist's works collected by the Joan Miró Foundation. Through Miró's representative works from his early years to his later years, it will review his creative career of more than 60 years and show the development of his artistic language and creative process. .

Sony Park Exhibition 2025 | Ginza Sony Park
The newly launched "Ginza Sony Park" has officially opened on January 26, 2025 (Sunday), and the first wave of planning activities "Sony Park Exhibition 2025" will be held simultaneously. With the theme of Sony's six major fields of music, semiconductors, finance, games, entertainment technology and movies, six groups of artists including YOASOBI, Sheep Literature, Vaundy, BABYMONSTER, Creepy Nuts, and Kensuke Ushio will be invited to participate in the creation, using art and high technology to create amazing experiences. Exhibiting works, the event will be divided into two stages, with three groups of works on display in each stage.

30th Anniversary of the Opening of the Museum Ryudai Takano Kasbaba | Tokyo Photographic Art Museum
Ryudai Takano (1963-) is a photographer and artist who won the 31st Kimura Ihei Photography Award for his photo book "IN MY ROOM" (2005) and continues to work both in Japan and abroad. In addition to his works on the theme of sexuality, such as "IN MY ROOM," Takano also takes snapshots of everyday life, such as "Daily Photos" and "Kasubaba." Since the Great East Japan Earthquake, he has also been working on the theme of exploring the origins of photography, using "shadows" as a subject. The title of this exhibition, "Kasubaba," is a word coined by Takano and is the plural of the word for a place like kas (ba). We live in the midst of rapid change in the times, with large-scale natural disasters, global epidemics of infectious diseases, environmental destruction and urban development due to economic development. Takano accepts reality, which is not just beautiful, and presents the viewer with raw images of weak and ugly things as they are. Through Takano's works, we will be able to see anew the richness and chaos of the everyday life we live in, something that is familiar to us but that we do not look closely at. We hope that this exhibition, which surveys Takano's career, including works shown for the first time, will provide some hints for surviving this everyday life, from which it is becoming increasingly difficult to see an exit.

Special Exhibition "Ramen Bowl Exhibition" | 21_21 DESIGN SIGHT
This exhibition was initiated by the Mino Ramen Bowl Exhibition, one of the Mino ware projects Sato and Hashimoto have been working on since 2012. Mino ware is a general term for ceramics made in the western Tono region of Gifu Prefecture (Tajimi City, Toki City, Mizunami City), among other areas. In fact, 90% of ramen bowls in Japan are Mino ware. By looking at ramen bowls from various perspectives, Sato and Hashimoto have conveyed the history and background of Mino ware, which has a history of more than 1,300 years, the activities of its makers, and the richness that everyday tableware brings to our lives.

Hibiya Art Park 2025 Exhibition | Hibiya Park
Tokyo Metropolitan Government is promoting a new experience of visiting parks by combining seasonal flowers and light performances, and is implementing a project called "Flower and Light Movement". At Hibiya Park, following last year, this year will also show the new charm of the park through large-scale art installations that combine flowers, lights and art. This year, the content and exhibition period of the art installations will be further expanded. With the theme of "Hibiva ArtPark 2025 - Visit and go out for a month -", the exhibition period will be divided into two phases. The first phase will focus on public art,
Transformed Composition - Group together and see and travel -| (April 25 (Friday) to May 11 (Sunday)), and the second phase will focus on the performing arts ""Play"ing Catch - Gathering and practicing -" (May 17 (Saturday) to May 25 (Sunday)).

2025 LEE DONG WOOK FANMEETING | Tokyo International Forum

Grand Tournament (Sumo) | The May Tournament 2025 Day 3 (Sumida City) | Ryogoku Kokugikan
Explore The May Tournament Day 3 sporting information for 13th May, as well as links for Sumo Wrestling tickets and more with Fixture Calendar. The May Tournament, also known as the Natsu Basho, is one of the six annual Grand Sumo tournaments held by the Japan Sumo Association. This highly anticipated sporting event takes place at the Ryogoku Kokugikan stadium, also known as the Sumo Hall, located in Tokyo, Japan. The tournament consists of 15 days of intense sumo wrestling matches between the top professional sumo wrestlers from across Japan. These wrestlers, known as rikishi, belong to different stables or teams and compete for the coveted Emperor's Cup trophy. With a history dating back to the 17th century, the May Tournament continues to attract a global audience, making it one of the oldest and most prestigious sporting events in the world of sumo wrestling.
Information Source: fixturecalendar.com

Grand Tournament (Sumo) | The May Tournament 2025 Day 7 (Sumida City) | Ryogoku Kokugikan
Explore The May Tournament Day 7 sporting information for 17th May, as well as links for Sumo Wrestling tickets and more with Fixture Calendar. The May Tournament, also known as the Natsu Basho, is one of the six annual Grand Sumo tournaments held by the Japan Sumo Association. This highly anticipated sporting event takes place at the Ryogoku Kokugikan stadium, also known as the Sumo Hall, located in Tokyo, Japan. The tournament consists of 15 days of intense sumo wrestling matches between the top professional sumo wrestlers from across Japan. These wrestlers, known as rikishi, belong to different stables or teams and compete for the coveted Emperor's Cup trophy. With a history dating back to the 17th century, the May Tournament continues to attract a global audience, making it one of the oldest and most prestigious sporting events in the world of sumo wrestling.
Information Source: fixturecalendar.com

Formula E · R8 · Tokyo | Tokyo

Grand Tournament (Sumo) | The May Tournament 2025 Day 11 (Sumida City) | Ryogoku Kokugikan
Explore The May Tournament Day 11 sporting information for 21st May, as well as links for Sumo Wrestling tickets and more with Fixture Calendar. The May Tournament, also known as the Natsu Basho, is one of the six annual Grand Sumo tournaments held by the Japan Sumo Association. This highly anticipated sporting event takes place at the Ryogoku Kokugikan stadium, also known as the Sumo Hall, located in Tokyo, Japan. The tournament consists of 15 days of intense sumo wrestling matches between the top professional sumo wrestlers from across Japan. These wrestlers, known as rikishi, belong to different stables or teams and compete for the coveted Emperor's Cup trophy. With a history dating back to the 17th century, the May Tournament continues to attract a global audience, making it one of the oldest and most prestigious sporting events in the world of sumo wrestling.
Information Source: fixturecalendar.com

Sunshine City Okinawa Mensore Festa | Tokyo
The Okinawa Menso-re Festival is held in partnership with Onna Village in Okinawa Prefecture, leveraging local relationships that Sunshine Aquarium has built as part of its coral conservation projects since 2006. This year marks the 16th year of the event. During the event, you can experience Okinawan culture at various venues in Sunshine City, including the largest Okinawan product exhibition in Tokyo.
On the stage and beer terrace inside the venue, you can see families dining together, people dining alone, and the staff from Sunshine City in suits raising Orion beer and dancing the Kachashi dance to the sound of the Shawzin. The whole venue is shrouded in the atmosphere of Okinawa
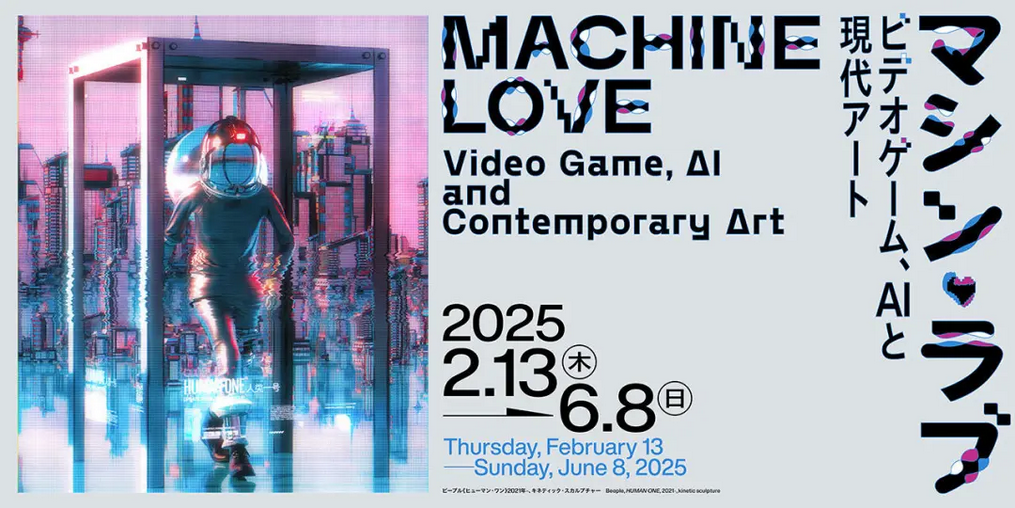
MACHINE LOVE: Video Game, AI and Contemporary Art | Mori Art Museum
With the explosive growth of artificial intelligence (AI) and the integration of virtual and real worlds, the latest cutting-edge technologies have quickly penetrated our daily lives. This tendency has become especially apparent since the COVID-19 pandemic, when many human activities shifted towards virtual space. Looking back, the progress of art and technology has run parallel to each other throughout the course of history, a phenomenon that is especially evident in the field of computer art and video art. While recent innovations in video game engines and AI offer unprecedented possibilities for artists, the advent of generative AI also has raised significant concerns. Such developments are now attracting considerable attention in various fields and industries, including the contemporary art world.

Tokyo Underground 1960s-1970s: A turning point in postwar Japanese culture | Mori Art Museum
From the late 1960s to the 1970s, the "underground," commonly known as "angura," took the Japanese art world by storm, mainly in the urban space of Tokyo. The underground, which replaced the "avant-garde" as the gathering point of cutting-edge art, was imported to Japan from the United States through experimental films and spread to fields such as fine art, music, manga, design, theater, and dance, becoming a trend recognized by the general public in just a few years. However, because it was established through its interaction with the anti-establishment movement of the time, it disappeared in the early 1970s as the movement declined. Although it was a short-lived phenomenon, underground culture had a great impact on postwar Japanese society, and it can be said that it remains as a style to this day. In addition, by its very nature, underground culture focused on temporary "events" rather than physical "works," and placed importance on the "places" that welcomed its bearers. For this reason, the underground is seen as the atmosphere of the times, and its actual nature has yet to be clarified. "MAM Research 011: Tokyo Underground 1960s-1970s - A turning point in postwar Japanese culture" will display many materials, mainly ephemera (printed material intended for temporary use), that are suited to conveying the rise and fall of underground culture in Tokyo. Furthermore, by examining these materials, we will attempt to look in detail at the history of "underground," its ideas and those who carried it, as well as its spread and limitations.

Perspectives - Maiko Haruki, Mari Katayama, Tomoko Yoneda | Mori Art Museum
"MAM Collection 019: Perspective" focuses on the photographic expressions of three female artists from the Mori Art Museum Collection: Maiko Haruki, Mari Katayama, and Tomoko Yoneda.
This exhibition introduces photographic works in which the image is completed through the viewer's involvement, rather than as a so-called recording medium. Maiko Haruki's series "either portrait or landscape" attempts to destabilize and liberate the viewer's perspective from the perspective of form, and also by incorporating the relationship between photography and abstract expression as a theme. Mari Katayama reverses the power relationship between image and viewer, challenging conventional traditional notions of diversity, normative values, and agency. Tomoko Yoneda's series "Between the Visible and the Invisible" expresses the interrelationship between the image on the surface and the narrative behind it.
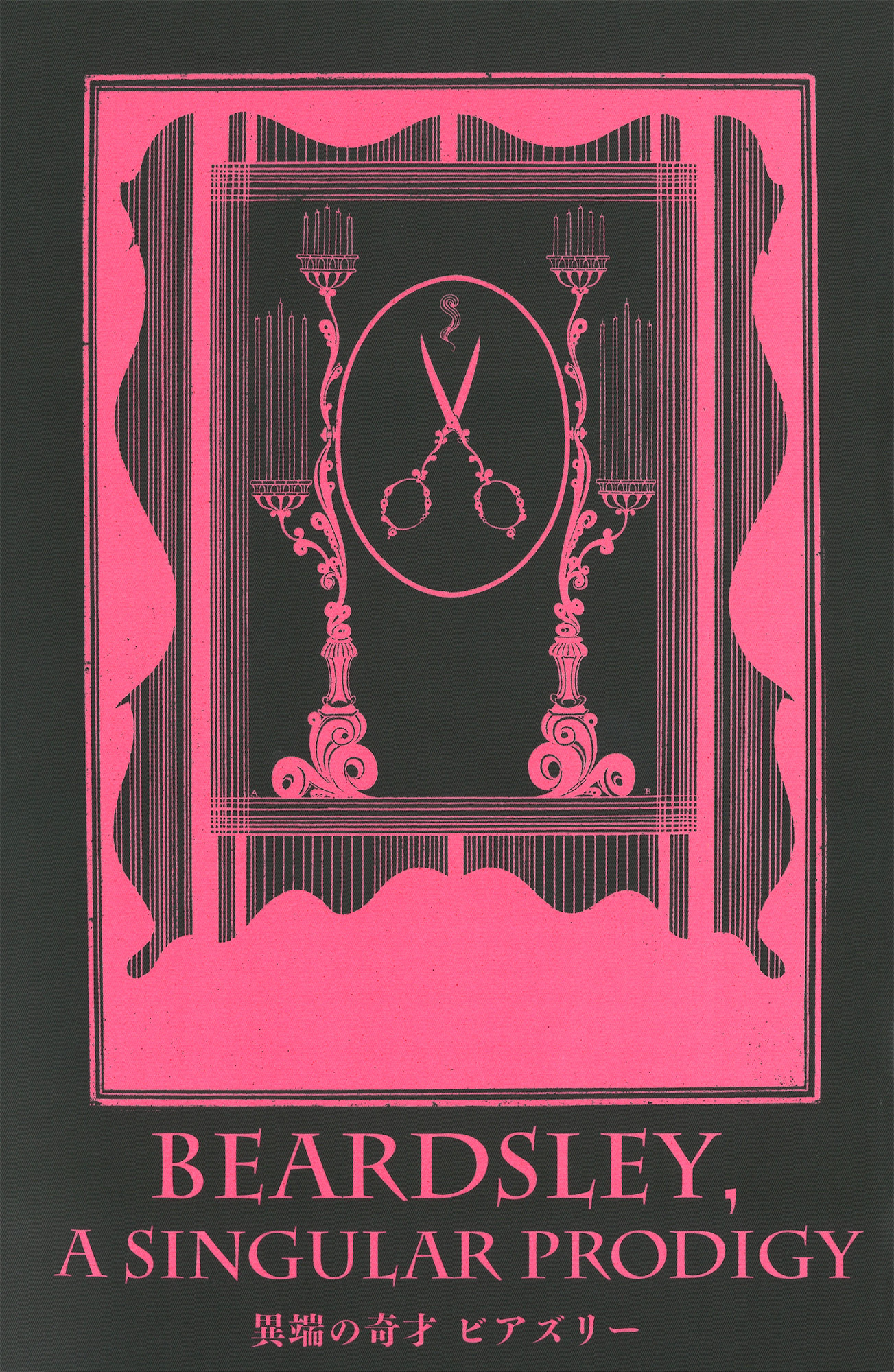
The heretical genius - Beardsley | Mitsubishi Ichigokan Museum
Aubrey Beardsley (1872-1898), a painter who died at the age of 25. This British genius continued to paint highly sophisticated works, consisting of precise line drawings and bold black and white color planes, by candlelight. This exhibition, organized jointly with the Victoria and Albert Museum (V&A), traces the path of Beardsley, who caused a stir in Europe and the United States at the end of the 19th century. The exhibition will feature approximately 220 pieces of Beardsley's art, including his breakthrough work Morte d'Arthur (1893-94) by Malory, Salome (1894) by Wilde, which is also well known in Japan, and his later masterpiece Mademoiselle de Maupin (1897) by Gautier, as well as illustrations and rare hand-drawn sketches from his early to later years, as well as colored posters and contemporary decorations.






